Advancing CO2 Separation through Polyphenylene Sulphide-Based Fillers: A Preliminary Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.137.1.116Keywords:
Biogas purification, membrane technology, polyphenylene sulphide, porous carbon, heteroatom dopingAbstract
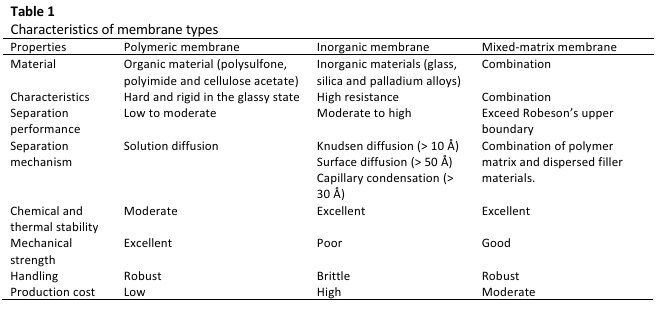
Efficient removal of Carbon dioxide from biogas, which is consist of methane (CH4) and CO2, is essential to achieve the biomethane standard of more than or similar 95% CH4. Conventional separation methods, such as cryogenic distillation, pressure swing adsorption and amine-based absorption, face significant challenges in terms of energy consumption, complexity and scalability. Membrane-based separation has emerged as a promising alternative, with polymeric membranes offering specific advantages for CO2 removal. However, traditional polymeric membranes encounter issues such as limited selectivity and compatibility, often requiring modifications or the incorporation of fillers. This review explores the innovative application of polyphenylene sulphide (PPS) including porous carbon materials derived from PPS (PCs) and nitrogen-sulphur co-doped (NSPCs) modifications, as organic fillers in polymers that focus on polysulfone membranes to enhance CO2 separation. This review presents state-of-the-art advancements in biogas separation membranes. PPS-based fillers offer the potential to overcome limitations associated with traditional inorganic fillers, providing improved separation efficiency, compatibility and sustainability. This review also discusses the broader implications of enhanced biogas utilization, emphasizing its relevance to sustainable energy goals and environmental policy. The integration of PPS-based fillers addresses limitations associated with conventional fillers, offering enhanced compatibility, increased separation efficiency and improved scalability. By supporting sustainable energy objectives and aligning with environmental policies, this approach offers a pathway toward next-generation membrane technologies for efficient, scalable and sustainable biogas purification.
Downloads