Chaotic Binary Manta-Ray Foraging Optimization Algorithm Based Descriptor Selection for Amphetamine-Type Stimulants Drug Classification
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.135.1.15Keywords:
binary manta ray foraging optimization, descriptor selection, chaotic map, drug classificationAbstract
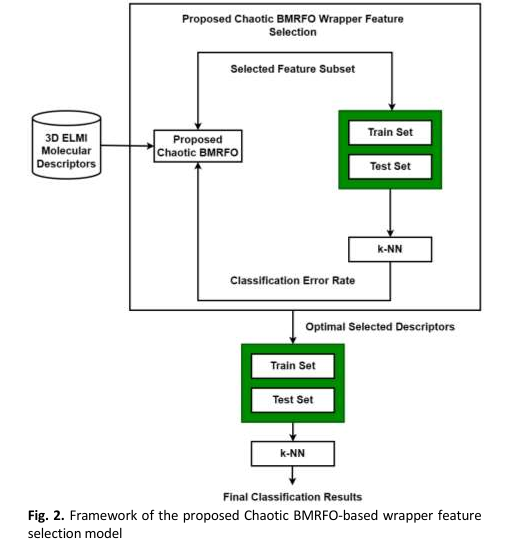
This study proposes a novel approach to optimize descriptor selection for classifying Amphetamine-Type Stimulants (ATS) and non-ATS drugs. The approach applies a Manta Ray Foraging Optimization (MRFO) framework enhanced with time-varying transfer function and a chaotic map. These enhancements aim to achieve a balance between exploration (finding new possibilities) and exploitation (refining promising solutions) within the improved version of binary MRFO (BMRFO) algorithm to solve descriptor selection problem. Two types of time-varying transfer functions recommended by earlier research are used to convert continuous MRFO to binary MRFO (BMRFO) for binary optimization problem. In addition, the pseudorandom number of the MRFO's probability operator is replaced with eleven different chaotic maps to prevent convergence problem. To evaluate the effectiveness of the suggested approach, a particular high-dimensional chemical dataset containing molecular descriptors of ATS and non-ATS drugs was utilized. The experimental results and statistical analysis show that the proposed BMRFOTV2-C9 employing the non-linear time-varying Sigmoid transfer function and Sinusoidal chaotic map is superior with lowest average fitness indicating its ability to convergence to optimal solution by selecting relevant descriptor subset and achieved better classification accuracy. Additionally, this study evaluated the performance of BMRFOTV2-C9 to other known BMRFO variations from the literature and the findings show that it is more efficient than others.
Downloads