Harmonic Reduction in Asymmetric Multilevel Inverters: A Dual Modulation Approach
Keywords:
Reduced-switch, multilevel inverter, Multicarrier PWM, Harmonic reduction, Switching optimization, THDAbstract
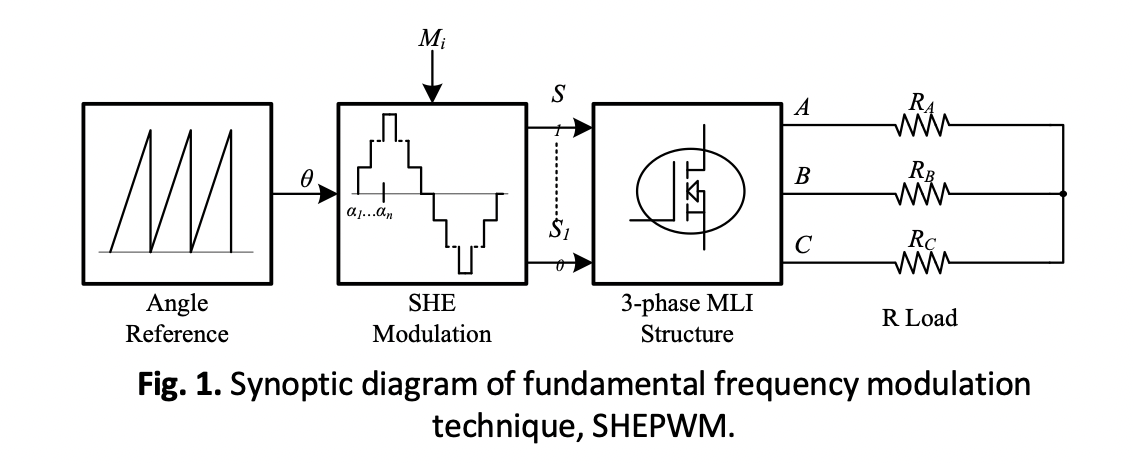
This paper addresses the challenge of optimizing the performance of asymmetric reduced multilevel inverters (ARSMLI) by achieving a compact inverter size while maintaining its output quality. The study examines the effectiveness of two modulation strategies: Selective Harmonic Elimination Pulse Width Modulation (SHEPWM) in low frequency operation and Multicarrier Pulse Width Modulation (MCPWM) in high frequency operation. The ARSMLI is modelled and simulated for 15 and 19-level inverters using the same circuit configuration, but with different DC source ratings. Simulation studies were conducted in PSIM software to evaluate the inverter performance using SHEPWM achieved through PSO-based optimization with a variable modulation index. The assessment is then repeated for MCPWM methods, such as Phase Disposition (PD), Phase Opposition Disposition (POD) and Alternate Phase Opposition Disposition (APOD). The main performance parameters: total harmonic distortion (THD) and output voltage quality, are analysed. The results show that APOD of MCPWM produced the highest output quality with the lowest THD, making it the optimal option for ARSMLI applications. In contrast, while SHEPWM provides efficient switching for a low frequency modulation, it cannot produce comparable THD. Nonetheless, both modulation strategies maintain THD performance below 5% in compliance with the IEEE 519 standard.
Downloads