Variable Frequency Drive of Induction Motor Using Various SPWM Technique
Keywords:
Sinusoidal pulse width modulation, induction motor, current waveform, electromagnetic torque, rotor speedAbstract
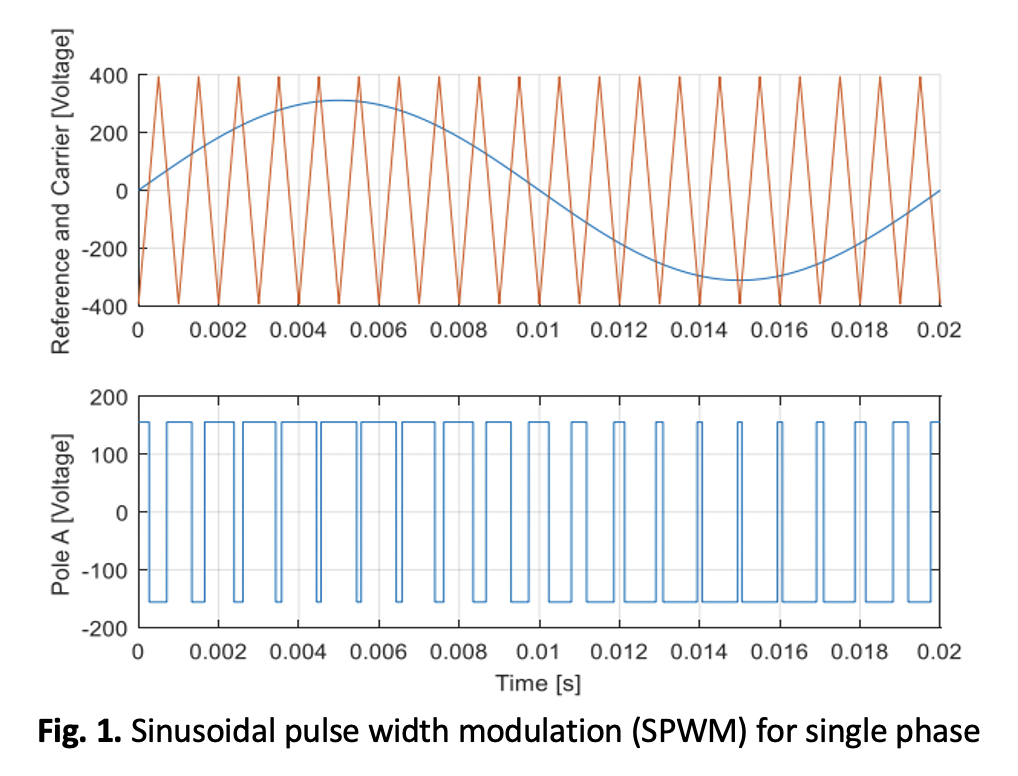
This paper presents the implementation of the Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM) technique for controlling an induction motor in a variable frequency drive (VFD) system. The SPWM technique generates sinusoidal three-phase alternating current (AC) by comparing the amplitudes of carrier and modulation waves, which is then applied to an induction motor (IM), specifically an asynchronous three-phase motor. Simulations are conducted to compare the performance of conventional Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and SPWM techniques in terms of current, electromagnetic torque, and rotor speed. The results indicate that the SPWM control technique provides greater stability for the induction motor system, especially during low-speed operation, where it reduces starting current and minimizes mechanical stress. The current waveform shows that the SPWM-controlled motor draws a significantly lower inrush current of 25A compared to the 37A drawn by the PWM-controlled motor. Similarly, the SPWM-controlled motor produces a starting torque of 16 Nm, compared to 32 Nm generated by the PWM-controlled motor. These findings suggest that SPWM offers superior performance at low speeds, mitigating the high inrush current associated with PWM, which can harm the motor over time. The SPWM technique demonstrates better control and stability for induction motors at low speeds, making it a more effective and reliable choice than PWM in applications where minimizing mechanical stress and enhancing motor longevity are critical.
Downloads