An Advanced Research Based on Machine Learning Techniques with Variant ARIMA Methods for Identifying Most Severity COVID-19 Data
Keywords:
new Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), confirmation case, time series model, autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), machine learning techniqueAbstract
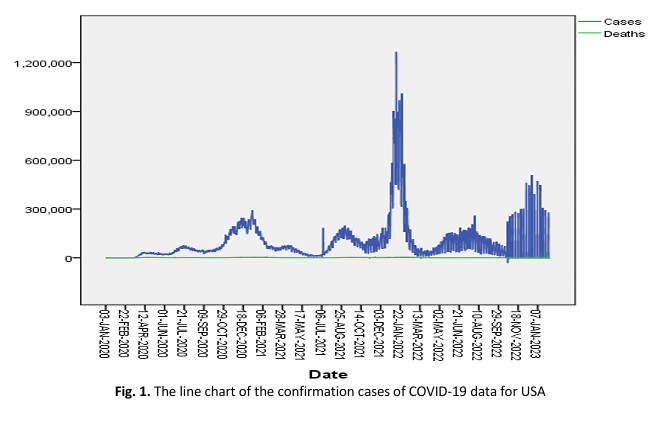
The COVID-19 epidemic has been a hot topic for a time-series forecasting in the last three years (2020-2022) data, and their national conditions and environmental backgrounds of different countries have different; thus, it is difficult but necessary to find a more suitable time-series model for prediction of relevant data within a short period of certain time. Therefore, tailored to countries to find out such an intelligent model to be able to predict the confirmation cases of coronavirus for different countries has an interesting and important challenge. COVID-19 studies have used traditional statistics-based research architectures, and there are several core problems: (1) it is lack of effectively organizing time-series forecasting models with machine learning techniques for COVID-19 data; (2) it may require different forecasting models depended on characteristics of different yearly COVID-19 data; (3) it is a valuable issue to find out a well-off forecasting model for modulating different parameters of COVID-19 data contexts. This study is trigged by such a research motivation to propose an integrated approach of different three time series-based models, such as autoregressive (AR), moving average (MA), and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), along with 12 machine learning models for addressing COVID-19 data applications. The study collects the data of confirmation cases from 2020-2022 and divides it into different sub-datasets from the most severities COVID-19 of countries to assess the effect of the proposed model. The evaluation standard is an effective indicator of mean absolute percentage error (MAPE). For the empirical results, it is found that different predictive techniques for the same country’s epidemic data have different prediction error rates; it is proved that different COVID-19 data of different countries needs different forecasting methods. The empirical results provide valuable information as a useful reference for different interest considerations to the interested parties. It is a good issue to differentiate from the existing works, the study highlights an organization method for three time-series models and 12 machine learning techniques in matching a COVID-19 data application; thus, this study has a clear contribution of a technical and applicable innovation on benefiting COVID-19 data fields.
Downloads