Exploring the Utilization of Reinforcement Learning Technique for Channel Accessibility in a Television White Space Database
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.133.1.6069Keywords:
Reinforcement learning, television white space, geolocation database, television white space databaseAbstract
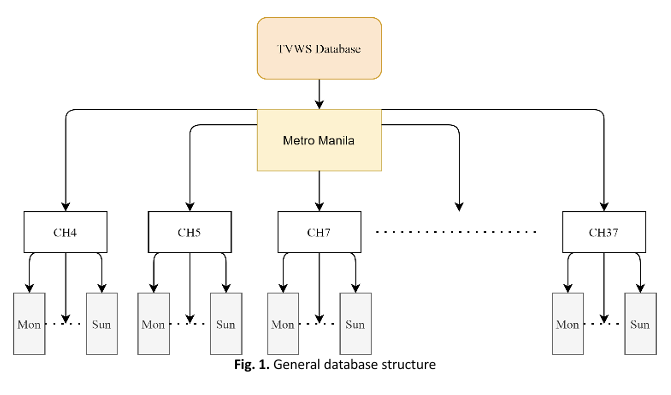
This study aimed to explore integrating the reinforcement learning (RL) technique into a television white space (TVWS) database using MATLAB. An RL implementation was developed to recommend the optimal channel to a secondary user (SU), considering the time of query, the transmitter power of the device, and the SU’s location. Data regarding the allocation of television frequencies within the Very High Frequency (VHF) and Ultra High Frequency (UHF) ranges was collected to compile the TV White Space database (TVWSDB). These entities were constructed using the 2019 edition of the National Telecommunications Commission's frequency allotment table. The database was structured to facilitate the RL utilization of the different data analysis functions in MATLAB after importing the data as workspace data. The database stored the primary user's (PU) location, transmitting power, height above average terrain (HAAT), frequency of operation, and programming schedule. Furthermore, a comparative analysis was conducted between a linear search algorithm and the AI program, revealing a significant performance advantage of the latter. Specifically, the RL-based program exhibited a speed improvement of 2080 times over the linear search algorithm.
Downloads