Multi-Criteria Assessment for Hydrogen-Based Decarbonisation Towards Net-Zero Emission for Eco-Industrial Parks in Malaysia
Abstract
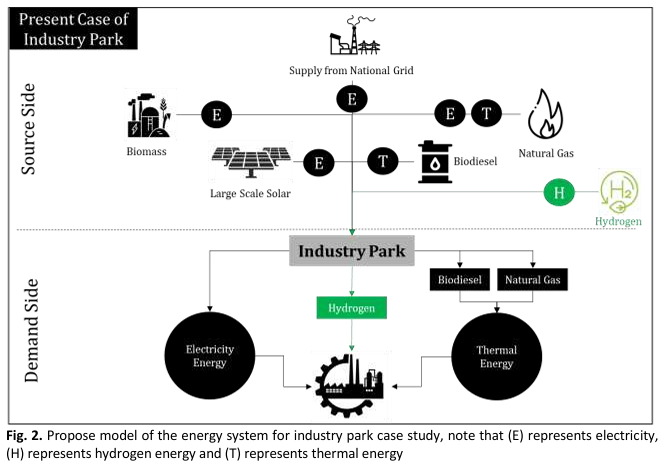
This study employs the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) methodology to conduct multi-criteria decision-making and determine the hydrogen-based energy transition model for the Eco-Industrial Park's decarbonization, based on the Malaysian industrial landscape. This research study is performed by incorporating the integration criteria of the industry supply chain and enabling parameters of funding, infrastructure, regulation, skills, and technology in the computational process of the AHP, and it is ranked accordingly. Two aspects are being considered for the hydrogen energy-based transition: the fuel switching option from the existing energy supply source at the industrial park comprising electricity and thermal, and the sustainable method for the hydrogen production source. The top three AHP results for the electricity and thermal energy indicated that the National Grid is ranked the highest at 0.87, followed by natural gas at 0.82 and biomass at 0.74 for the fuel switching into hydrogen for the energy transition. Meanwhile, the top three results for the hydrogen supply source indicated that the industrial park's best option for hydrogen production is the Green Hydrogen via electrolysis process from the Large-Scale Solar at 0.94. It is followed by Grey Hydrogen via Steam Methane Reforming from the natural gas source at 0.82 and Orange Hydrogen via biomass gasification at 0.82. The overall ranking process for the energy supply system at the industrial park provides a systematic priority and basis for the fuel switching strategy of the electricity and thermal energy and the best selection for hydrogen production towards the carbon emission reduction at the industrial park level. This method can assist the decision-makers in sustainability energy planning as part of the energy transition to transform the industrial park into an Eco-Industrial Park.
Downloads