Enhancing Medical Image Quality with Efficient Denoising Techniques Using Hybrid Methods
Keywords:
Medical image, denoising, wavelet, curveletAbstract
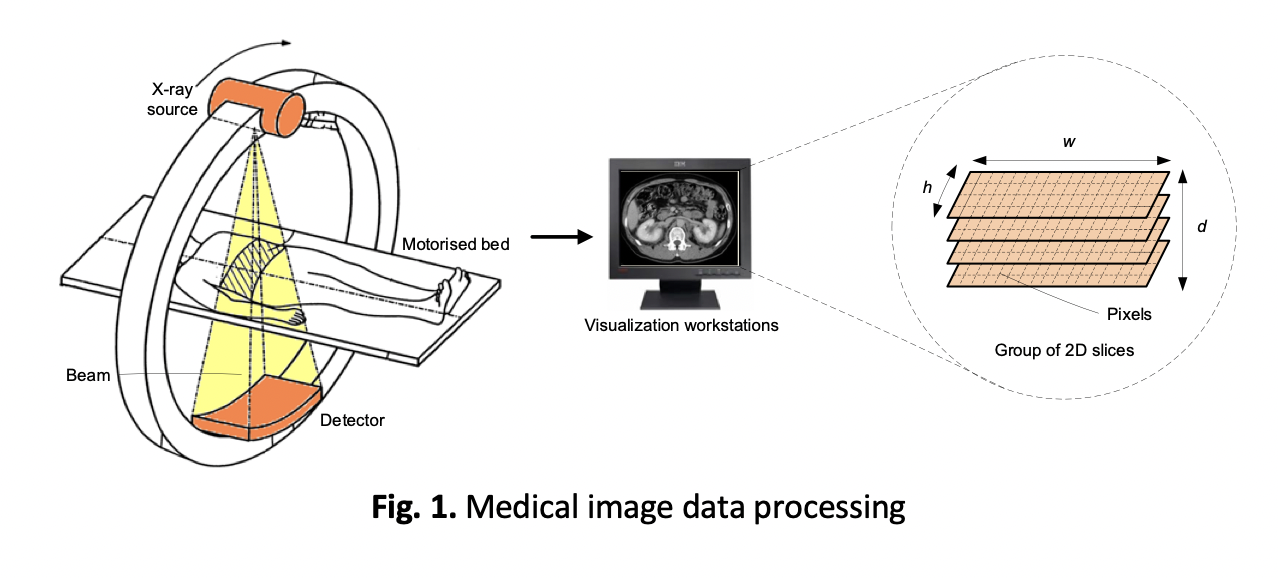
New technologies in the healthcare industry are revolutionizing the use of medical modalities, from simple measurement devices to complex systems like Computed Tomography (CT) scanners, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Positron Emission Tomography (PET), and Ultrasound machines. However, the medical imaging acquisition process and subsequent processing stages can introduce noise and artifacts, which can adversely affect the accuracy of medical diagnoses and treatments. This paper presents the development of an enhanced denoising technique using a hybrid method that combines Fast Discrete Wavelet Transform (FDWT) and Fast Discrete Curvelet Transform (FDCvT) algorithms. The limitations of wavelets in handling curves and edges are mitigated by the curvelet transform, thereby directly improving imaging performance. Three different approaches, based on various wavelet families, are proposed: Daubechies (Approach-1), Coiflet (Approach-2), and Biorthogonal (Approach-3) wavelet transforms. To create a robust denoising system, Gaussian noise is added to the original images. The noisy images are first decomposed into several sub-bands using the FDWT algorithm. The wavelet coefficients generated are then separated into different orientations using the wrapping-based FDCvT algorithm. These wavelet coefficients are wrapped around a periodic extension of themselves. By effectively addressing the limitations of wavelets in handling curves and edges, the hybrid method enhances imaging performance across various medical modalities, including MRI, CT, and PET. The evaluation using Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) confirms that the proposed approaches significantly outperform existing benchmark techniques. Specifically, Approach-2 shows a 25 % reduction in noise for CT images, while Approach-3 yields a substantial 15 % improvement in Gaussian denoising. These findings highlight the potential of the hybrid method to improve the accuracy and reliability of medical diagnoses and treatments by reducing noise and artifacts in medical images.
Downloads