Evaluating the Adsorption Efficiency of Pelletized and Powdered Clinoptilolite for Methylene Blue
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.143.1.19Keywords:
Adsorption capacity, clinoptilolite, natural zeolite, methylene blue, pelletized, tabletAbstract
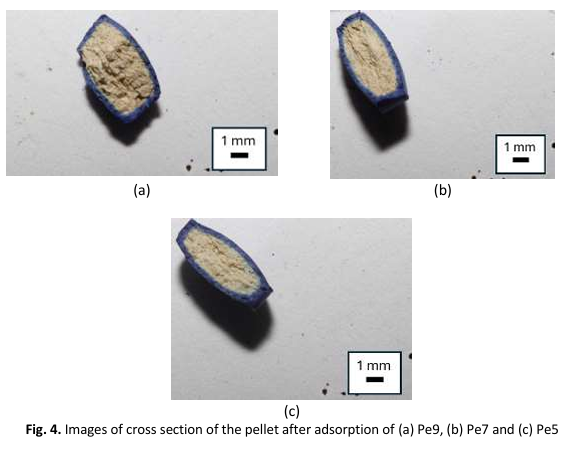
The widespread use of dyes in various industries such as clothing, manufacturing, cosmetics, and printing has raised concerns about their negative impact on the environment. Adsorption is a practical method used in industries to treat this type of discharge on a large scale. However, the conventional powder format raises practical concern. This paper examines the adsorption capacity of clinoptilolite prepared as both pellets and powders for removing methylene blue. Both formats showed a consistent increase in adsorption capacity as the mass increased due to the increased number of adsorption sites attracting the methylene blue. However, compared to the powder format, the adsorption capacity of the pelletized clinoptilolite was significantly lower as the mass increased. The difference in adsorption capacity between the pellet and powder widened with increasing mass. This is because increasing the pellet mass only contributes to small increases in surface area from the slight increase in pellet thickness, whereas the powder format effectively uses all the exposed surface area of each powder unit as adsorption sites. Additionally, the methylene blue does not completely penetrate the inner structure of the pellet, further lowering its adsorption capacity. This study suggests that the adsorption capacity of clinoptilolite pellets can be enhanced to match the performance of the powder format if the mass is decreased. It shows that there is significant potential for improving clinoptilolite pellets to perform as well as the powder format.
Downloads