Exploratory Data Analysis and Energy Intensity Forecasting at Water Treatment Plant
Keywords:
Energy intensity, Exploratory data analysis, Forecasting, Univariate time series, Water treatment plantAbstract
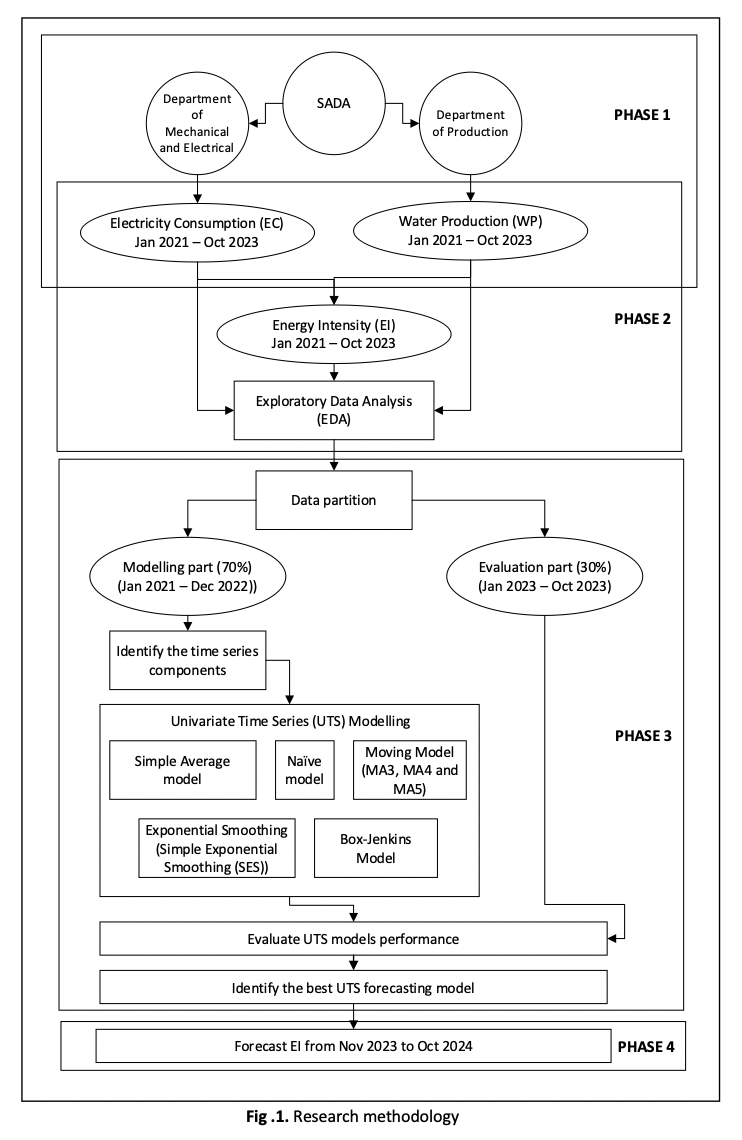
Energy intensity optimization in water treatment plants (WTPs) is essential for ensuring sustainable operations and cost-effective resource management. In Malaysia, WTPs consume substantial energy to maintain water treatment and distribution, yet inefficiencies in energy usage remain a concern. This study integrates Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) and Univariate Time Series (UTS) forecasting to analyze and predict energy intensity trends at four WTPs in Northern Kedah Region One. The primary objective is to enhance energy efficiency by identifying consumption patterns and selecting the most suitable forecasting model for energy intensity prediction. The methodology involved data collection on electricity consumption and water production from January 2021 to October 2023, followed by EDA to detect patterns, anomalies, and relationships in energy usage. Several UTS models, including Naïve, Moving Average, Simple Exponential Smoothing, and ARIMA, were applied to forecast energy intensity. The results highlight significant variations in energy intensity among the WTPs, with Jenun Baru exhibiting the lowest energy intensity, indicating greater efficiency, while Jeneri recorded the highest. Furthermore, findings demonstrate that no single forecasting model is universally optimal, as performance varies based on data characteristics. This study underscores the importance of incorporating EDA in forecasting to improve forecasting model accuracy and support informed decision-making in WTP operations. The insights derived from this research can guide policymakers and industry practitioners in implementing energy-saving strategies and optimizing water treatment processes. Future research should explore multivariate time series models that incorporate external factors such as weather conditions and operational changes to enhance forecasting precision and energy efficiency.
Downloads