Production of Sustainable Bioplastic Derived from Renewable Lignocellulosic Agricultural Biomass: A Comprehensive Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/fwe.4.1.114Keywords:
Lignocellulose, Bioplastics, Nanocellulose, Biodegradable polymers, Cellulose, BiomaterialsAbstract
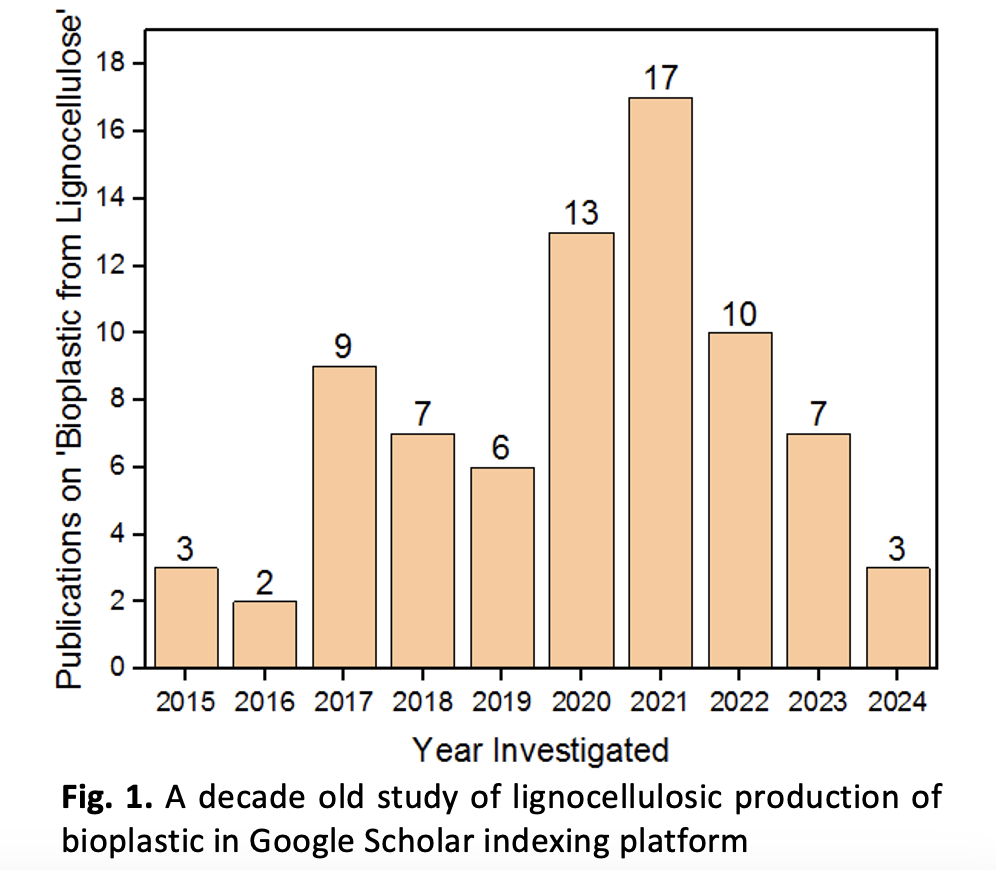
Environmental pollution is increasing due to plastic materials which may find their way into our food. Now, lignocellulose materials offer enormous potential for use in the production of eco-friendly bioplastics and decreasing the environmental impact of fossil fuels. These raw materials can be used to separate lignin and cellulose. Research on bioplastics, derived from biological sources is currently gaining attention for greener environment. Through surface alterations and other chemical derivatizations, several materials are readily adaptable to the production of diverse bioplastics. Polyhydroxyalkanoates, bio-polyethylene, polyurethanes, and nano cellulosic bioplastics are examples of common bio-based polymers produced from lignin or cellulose. The current review covers lignocellulose compositions, bioplastic manufacturing methods, and applications in a range of industries. Bioplastics made from lignocellulose will become a useful material in a variety of industries in no distant time. On the hand, bio composites from food sources are currently being recognized and researched.