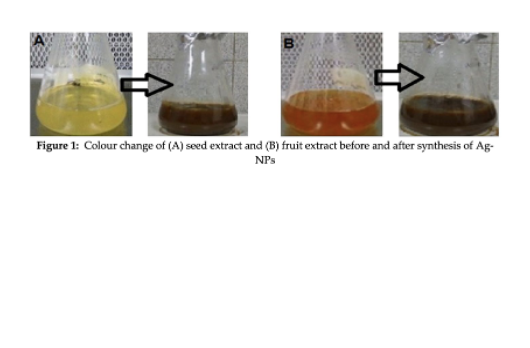
Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles from Bitter Melon (Momordica Charantia) Fruit and Seed Extract and their Antimicrobial Activity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.2.1.111Keywords:
Green synthesis, Silver nanoparticle, Antimicrobial, Momordica charantiaAbstract
Momordica charantia is a phenolic rich vegetable. In this study, the fruits and seeds extract of M. charantia were used to synthesize silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) using biotechnological approach. Structural, morphological, and antimicrobial properties of the synthesized Ag-NPs were characterized using UV/Vis Spectrophotometry, Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), High Resolution Transmission Electronics Microscopy (HRTEM), Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-Ray diffraction (XRD). In DLS, the average particle size of Ag-NPs was found 17.5 ± 2.1 nm and 18.3 ± 1.9 nm using seed and fruit extract, respectively. HRTEM has revealed their spherical structure for both seed and fruit extract of M. charantia. FESEM images found Ag-NPs with the size between ~20 and ~35 nm. The Ag NPs exhibited Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) centered at 405 nm for seed extract and 402 nm for fruit extract using a UV–visible spectrophotometer. FT-IR results showed phenolic and carbohydrate compounds involved in the synthesis of the Ag NPs. Furthermore, the synthesized Ag NPs has found highly rich in antibacterial properties against Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium. Thus, bioconversion of Ag NPs by M. charantia could be employed as a potential antibacterial source to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms from agricultural and food preservation industry.
Downloads
References
B. Ankamwar, M. Chaudhary and M. Sastry. Gold nanotriangles biologically synthesized using tamarind leaf extract and potential application in vapor sensing. Synth. React. Inorg. M., 2005, 35(1), pp. 19-26. doi: 10.1081/SIM-200047527.
H. Jahangirian, M. H. S. Ismail, M. J. Haron, R. Rafiee-Moghaddam, K. Shameli and S. Hosseini. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite/Fe3O4 nanocomposite by green quick precipitation method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct., 2013, 8.(4), pp. 1405-1413.
M. Irfan, M. Saeed, B. Iqbal, M. Ghazanfar. Application of Plant-Based Natural Product to Synthesize Nanomaterial. Nanomaterials in Biofuels Research, Clean Energy Production Technologies, 2020, Springer. pp. 29-52. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9333-4_12.
R. Khandanlou, M. Ahmad, H. R. Fard Masoumi, K. Shameli and M. Basri, Rapid adsorption of copper (II) and lead (II) by rice straw/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: optimization, equilibrium isotherms, and adsorption kinetics study. PloS one., 2015, 10.(3), pp. 1-19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120264.
A. Amini, M. Latifi, and J. Chaouki. Electrification of materials processing via microwave irradiation: A review of mechanism and applications. Appl. Therm. Eng., 2021, pp. 117003. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117003.
Z. Izadiyan, K. Shameli, M. Miyake, H. Hara, S. H. Mohd Taib and E. Rasouli, Cytotoxicity assay of plant-mediated synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using Juglans regia green husk extract. Arab. J. Chem., 2020, 13.(1), pp. 2011-2023. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.02.019.
P. Singh, Y. J. Kim, D. Zhang, D. C. Yang. Biological synthesis of nanoparticles from plants and microorganisms. Trends Biochem. Sci., 2016. 34(7): pp. 588-599. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.006.
R. Khandanlou, M. Ahmad, K. Shameli and K. Kalantari, Synthesis and characterization of rice straw/Fe3O4 nanocomposites by a quick precipitation method. Molecules, 2013, 18.(6), 6597-6607. doi: 10.3390/molecules18066597.
A. K. Ojha, J. Rout, S. Behera, and P. L. Nayak. Green synthesis and characterization of zero valent Ag-NPs from the leaf extract of Datura metel. Int. J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2013. 2(1), pp. 31-35.
K. X. Lee, K. Shameli, Y. P. Yew, S. Y. Teow, H. Jahangirian, R. Rafiee-Moghaddam and T. J. Webster. Recent developments in the facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and their biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed., 2020, 15, pp. 275-300. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S233789.
S. Ahmed, M. Ahmad, B. L. Swami, S. Ikram. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of Ag-NPs for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J. Adv. Res., 2016, 7(1), pp. 17-28. doi. 10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007.
P. Shabanzadeh, N. Senu, K. Shameli, F. Ismail, A. Zamanian, and M. Mohagheghtabar. Prediction of silver nanoparticles’ diameter in montmorillonite/chitosan bionanocomposites by using artificial neural networks. Res. Chem. Intermed., 2015, 41(5), pp. 3275-3287. doi: 10.1007/s11164-013-1431-6.
B. Ajitha, Y. A. K. Reddy, and P. S. Reddy. Biosynthesis of Ag-NPs using Momordica charantia leaf broth: evaluation of their innate antimicrobial and catalytic activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B., 2015, 146, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.02.017.
P. Shabanzadeh, R. Yusof, and K. Shameli. Modeling of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in Vitex negundo L. extract by artificial neural network. RSC Advances., 2015, 5(106), pp. 87277-87285. doi: 10.1039/C5RA11940E.
J. Grover, and S. Yadav. Pharmacological actions and potential uses of Momordica charantia: a review. J. Ethnopharmacol., 2004, 93(1), pp. 123-132. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.03.035.
P. Shabanzadeh, N. Senu, K. Shameli and M. Mohaghegh Tabar. Artificial intelligence in numerical modeling of silver nanoparticles prepared in montmorillonite interlayer space. J. Chem., 2013, 2013, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.1155/2013/305713.
S. K. Balavandy, K. Shameli, and Z. Z. Abidin, Rapid and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via sodium alginate media. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2015., 2015, 10.(1), 486-497.
P. Budrat, and A. Shotipruk. Enhanced recovery of phenolic compounds from bitter melon (Momordica charantia) by subcritical water extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol., 2009, 66(1), pp. 125-129. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2008.11.014.
C. Marambio-Jones, and E.M. Hoek, A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanoparticle Res., 2010, 12(5), pp. 1531-1551. doi: 10.1007/s11051-010-9900-y.
K. Shameli, M. Ahmad, S. D. Jazayeri, P. Shabanzadeh, H. Jahangirian, M. Mahdavi, and Y. Abdollahi. Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol mediated silver nanoparticles by the green method. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2012, 13(6 ), pp. 6639-6650. doi: 10.3390/ijms13066639.
A. R. Shahverdi, A. Fakhimi, H. R. Shahverdi, S. Minaian. Synthesis and effect of Ag-NPs on the antibacterial activity of different antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Nanomedicine: NBM., 2007, 3(2), pp. 168-171. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2007.02.001.
M. Rafique, I. Sadaf, M. S. Rafique, M. B. Tahir. A review on green synthesis of Ag-NPs and their applications. Artif. Cell Nanomed. B., 2017, 45(7), pp. 1272-1291. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2016.1241792.
S. Basavaraja, S. D. Balaji, A. Lagashetty. Extracellular biosynthesis of Ag-NPs using the fungus Fusarium semitectum. Mater. Res. Bull., 2008, 43(5), pp. 1164-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2007.06.020.
S. Shrivastava, T. Bera, S. K. Singh, G. Singh, P. Ramachandrarao, and D. Dash. Characterization of antiplatelet properties of silver nanoparticles. ACS nano., 2009. 3(6), pp. 1357-1364. doi: 10.1021/nn900277t.
V. K. Sharma, R. A. Yngard, and Y. Lin. Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Advances in colloid and interface science, 2009, 145(1-2), pp. 83-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2008.09.002.
K. Shameli, M. Ahmad, S. D. Jazayeri, P. Shabanzadeh, P. Sangpour, H. Jahangirian, Y. Gharayebi. Investigation of antibacterial properties silver nanoparticles prepared via green method. Chem. Cent. J., 2012, 6(1), pp. 73(1-10). doi: 10.1186/1752-153X-6-73.
M. Ahmad, J. J. Lim, K. Shameli, N. A. Ibrahim, M. Y. Tay, B. W. Chieng. Antibacterial activity of silver bionanocomposites synthesized by chemical reduction route. Chem. Cent. J., 2012, 6(1), pp. 101(1-9). doi: 10.1186/1752-153X-6-101.
G. Singhal, R. Ghavesh, K. Kasariya. Biosynthesis of Ag-NPs using Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi) leaf extract and screening its antimicrobial activity. J. Nanoparticle Res., 2011, 13(7), pp. 2981-2988. doi: org/10.1007/s11051-010-0193-y.