Circularly Polarised Laser Ablation in Liquids (CP-LAL)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.10.1.721Keywords:
Chiral Nanoparticles, Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid, Circularly Polarized Light, Light-Matter Interaction, Chirality TransferAbstract
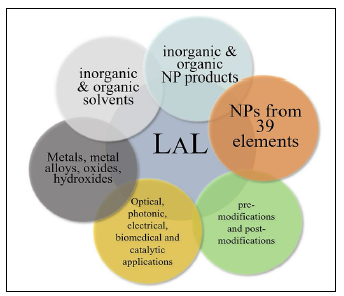
Chirality, a fundamental property of molecules, has garnered significant interest in recent years due to its implications in various technological and scientific advancements. Chiral nanoparticles (CNPs) provide an elegant route to combine the advantages of two worlds; the widespread applications of NPs and the specific benefits, gained due to their chirality generating a large body of opportunities, such as better performance of NPs in biological applications or circularly polarized light (CPL) emitters or high-surface features that are asymmetric catalysts to name a few. Accordingly, large-scale production of CNPs is an obvious demand, which is not easy to be realized with the methods that are commonly used, due to CNPs being either highly material specific or not easily scalable. We suggest the use of circularly polarized light for laser ablation in liquids (CP-LAL) as a chiral variant of LAL to fabricate CNPs, specifically benefiting from the advantageous properties of LAL such as scalability, universality, and green-synthesis principles conformity. The combination of circularly polarized light with laser ablation in liquid techniques (CP-LAL) presents a novel means of exploring the tangled relationships between circularly polarised light and chiral nanoparticle formation, paving the way for innovative applications and deeper insights into the fundamental light-matter interactions.
Downloads