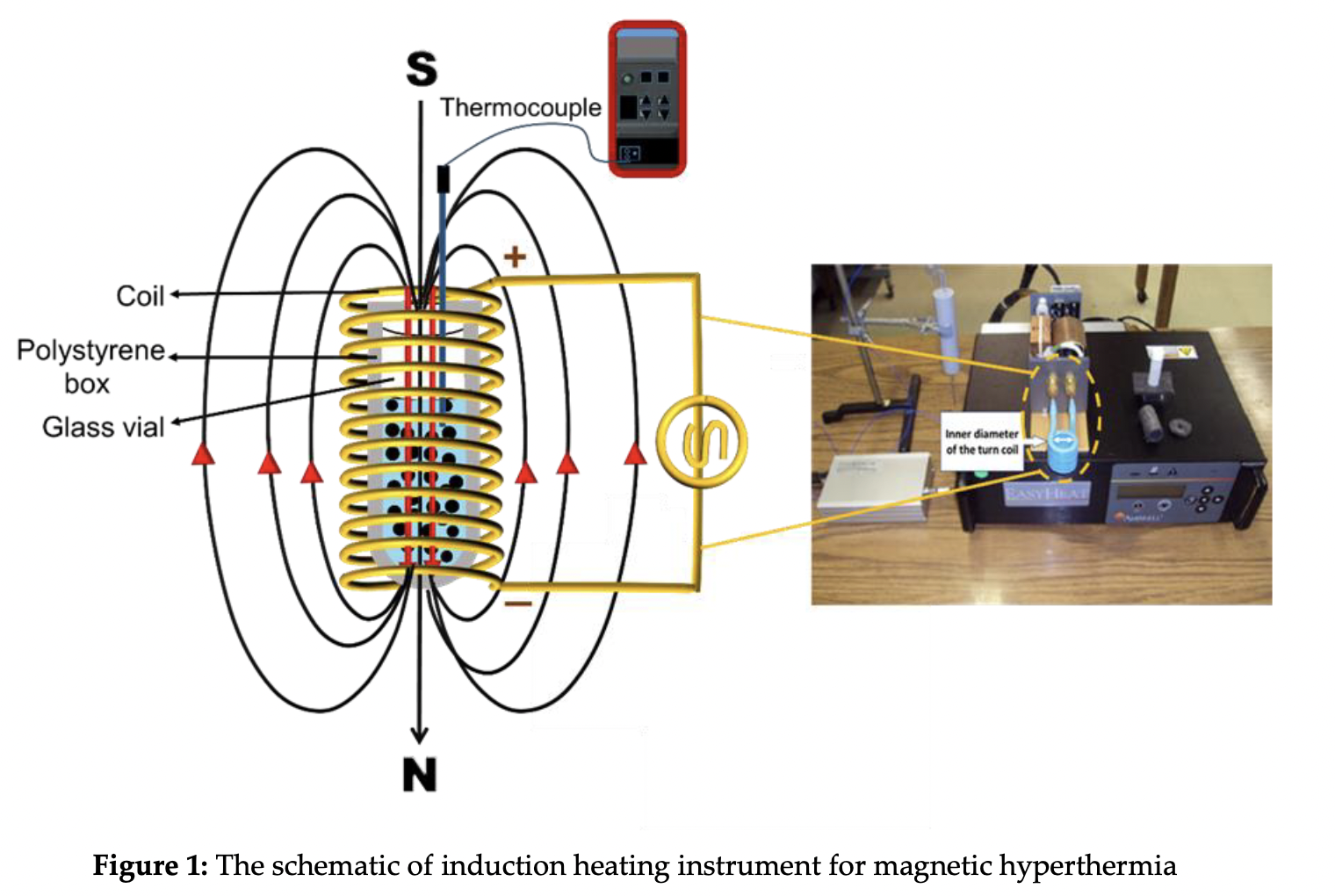
Magnetic Nanoparticles In Hyperthermia Therapy: A Mini-Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.2.1.5160Keywords:
Magnetic Nanoparticles, Magnetic Hyperthermia, Nanofluids, Cancer TherapyAbstract
The activation of MNPs for hyperthermia therapy via an external alternating magnetic field is an interesting method in targeted cancer therapy. This mini-review explains new developments and implications of magnetic nanofluids mediated magnetic hyperthermia for their potential use in future clinical settings. The external alternating magnetic field generates heat in the tumor area to eliminate cancer cells. Depending on the tumor type and targeted area, several kinds of MNPs with different coating agents of various morphology and surface charge have been developed. The tunable physiochemical characteristics of MNPs enhance their heating capability. In addition, heating efficiency is strongly associated with the amount of the applied magnetic field and frequency. The great efforts have offered promising preclinical trials of magnetic hyperthermia via MNPs as a smart nanoagent. MNPs are very appropriate to be considered as a heating source in MHT and prospective research in this field will lead to tackle the problems from chemotherapy and introduce promising therapeutic techniques and nanodrug formulations for remotely controlled drug release and anticancer effects. This mini-review aims to pinpoint synthesis and structural analysis of various magnetic nanoparticles examined for magnetic hyperthermia therapy and controlled drug release in cancer treatment.
Downloads
References
Sukri SNAM, Shameli K, Wong MM-T, Teow S-Y, Chew J, Ismail NA. Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities of plant-mediated synthesized zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Punica granatum (pomegranate) fruit peels extract. J. Mol. Struct. 2019;1189:57-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.026.
Ismail NA, Shameli K, Wong MM-T, Teow S-Y, Chew J, Sukri SNAM. Antibacterial and cytotoxic effect of honey mediated copper nanoparticles synthesized using ultrasonic assistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019;104:109899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109899.
Harun, M.A., N.A.C. Sidik, and M.A.M. Rohaizan, A Review on Stability and Heat Transfer Performance of Nanofluid Using Surfactants. Journal of Advanced Research in Materials Science, 2020. 75(1): p. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.37934/arms.75.1.19.
Yusefi M, Shameli K, Jahangirian H, et al. The Potential Anticancer Activity of 5-Fluorouracil Loaded in Cellulose Fibers Isolated from Rice Straw. International journal of nanomedicine. 2020;15:5417.
Yusefi M, Shameli K. Nanocellulose as a Vehicle for Drug Delivery and Efficiency of Anticancer Activity: A Short-Review. Journal of Research in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 2021;1(1):30-43. https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.1.1.3043.
Hamrayev H, Shameli K, Yusefi M. Preparation of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and its Cancer Treatment Effects: A Review Paper. Journal of Advanced Research in Micro and Nano Engineering. 2020;2(1):1-11.
Boyle P, Levin B. World cancer report 2008. IARC Press, International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008.
Mühlberger M, Janko C, Unterweger H, et al. Functionalization of T lymphocytes for magnetically controlled immune therapy: selection of suitable superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019;473:61-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.10.022.
Atta AH, El-ghamry MA, Hamzaoui A, Refat MS. Synthesis and spectroscopic investigations of iron oxide nano-particles for biomedical applications in the treatment of cancer cells. J Mol Struct. 2015;1086:246-254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.12.085.
Arsalani S, Guidelli EJ, Silveira MA, et al. Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated by natural rubber latex as MRI contrast agent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019;475:458-464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.11.132.
Yusefi M, Shameli K, Hedayatnasab Z, et al. Green synthesis of Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia, magnetic resonance imaging and 5-fluorouracil carrier in potential colorectal cancer treatment. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021:1-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04388-1.
Hedayatnasab Z, Dabbagh A, Abnisa F, Daud WMAW. Polycaprolactone-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for In Vitro Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy of Cancer. Eur. Polym. J. 2020:109789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109789.
Yusefi M, Shameli K, Yee OS, et al. Green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles stabilized by a Garcinia mangostana fruit peel extract for hyperthermia and anticancer activities. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2021;16:2515. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S284134.
Huang C, Soenen SJ, Rejman J, et al. Magnetic electrospun fibers for cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012;22(12):2479-2486. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201102171.
Senapati S, Mahanta AK, Kumar S, Maiti P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018;3(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-017-0004-3.
Zhao Q, Wu Q, Ma P, et al. Selective and sensitive fluorescence detection method for pig IgG based on competitive immunosensing strategy and magnetic bioseparation. Talanta. 2019;195:103-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.11.041.
Nikitin M, Orlov A, Znoyko S, et al. Multiplex biosensing with highly sensitive magnetic nanoparticle quantification method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018;459:260-264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.10.078.
Ye D, Li Y, Gu N. Magnetic labeling of natural lipid encapsulations withiron-based nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2018:1-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-1980-5.
Li W, Fan G-C, Gao F, Cui Y, Wang W, Luo X. High-activity Fe3O4 nanozyme as signal amplifier: A simple, low-cost but efficient strategy for ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019;127:64-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.11.043.
Lu AH, Salabas EeL, Schüth F. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46(8):1222-1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866.
Yusefi M, Shameli K, Jumaat AF. Preparation and Properties of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: A Brief Review. Journal of Advanced Research in Materials Science. 2020;75(1):10-18. https://doi.org/10.37934/arms.75.1.1018.
Yusefi M, Shameli K, Ali RR, Pang S-W, Teow S-Y. Evaluating anticancer activity of plant-mediated synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using Punica Granatum fruit peel extract. J. Mol. Struct. 2020;1204:127539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127539.
Jahangirian, H., et al., Green synthesis of zeolite/Fe2O3 nanocomposites: Toxicity & Cell proliferation assays and application as a smart iron nanofertilizer. Int. J. Nanomedicine, 2020. 15: p. 1005. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S231679.
Wu W, Wu Z, Yu T, Jiang C, Kim W-S. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2015;16(2):023501. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/16/2/023501.
Reddy LH, Arias JL, Nicolas J, Couvreur P. Magnetic nanoparticles: design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012;112(11):5818-5878. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300068p.
Zahedi-Tabar Z, Bagheri-Khoulenjani S, Amanpour S, Mirzadeh H. A Review on the Application of In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Cancerous Tumors for the Study of the Hyperthermia Effect. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.18502/bccr.v11i1.1653.
Hedayatnasab Z, Abnisa F, Daud WMAW. Review on magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic nanofluid hyperthermia application. Mater. Des. 2017;123:174-196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.036.
Evans BA, Bausch MD, Sienerth KD, Davern MJ. Non-monotonicity in the influence of nanoparticle concentration on SAR in magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018;465:559-565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.06.051.
Giustini AJ, Petryk AA, Cassim SM, Tate JA, Baker I, Hoopes PJ. Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in cancer treatment. Nano Life. 2010;1(01n02):17-32. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793984410000067.
Hedayatnasab Z, Dabbagh A, Abnisa F, Daud WMAW. Synthesis and In-vitro Characterization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using a Sole Precursor for Hyperthermia Therapy. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020:110975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.110975.
Laurent S, Dutz S, Häfeli UO, Mahmoudi M. Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: focus on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011;166(1-2):8-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.04.003.
Nieciecka D, Celej J, ?uk M, et al. Hybrid System for Local Drug Delivery and Magnetic Hyperthermia Based on SPIONs Loaded with Doxorubicin and Epirubicin. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(4):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040480.
Shanmuganathan R, LewisOscar F, Shanmugam S, et al. Core/shell nanoparticles: synthesis, investigation of antimicrobial potential and photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. JPPBEG. 2020;202:111729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111729.
Sahu NK, Gupta J, Bahadur D. PEGylated FePt–Fe3O4 composite nanoassemblies (CNAs): in vitro hyperthermia, drug delivery and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Dalton trans. 2015;44(19):9103-9113. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT03470H.
Kossatz S, Grandke J, Couleaud P, et al. Efficient treatment of breast cancer xenografts with multifunctionalized iron oxide nanoparticles combining magnetic hyperthermia and anti-cancer drug delivery. BCR. 2015;17(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-015-0576-1.
Yao X, Niu X, Ma K, et al. Graphene quantum dots?capped magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a multifunctional platform for controlled drug delivery, magnetic hyperthermia, and photothermal therapy. Small. 2017;13(2):1602225. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201602225.
Peigneux A, Oltolina F, Colangelo D, et al. Functionalized biomimetic magnetic nanoparticles as effective nanocarriers for targeted chemotherapy. Part Part Syst Charact. 2019;36(6):1900057. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.201900057.
Ullah S, Seidel K, Türkkan S, et al. Macrophage entrapped silica coated superparamagnetic iron oxide particles for controlled drug release in a 3D cancer model. J. Control. Release. 2019;294:327-336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.12.040.
Cho H-Y, Lee T, Yoon J, et al. Magnetic oleosome as a functional lipophilic drug carrier for cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2018;10(11):9301-9309. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b19255.
Wang Y-J, Lin P-Y, Hsieh S-L, et al. Utilizing Edible Agar as a Carrier for Dual Functional Doxorubicin-Fe3O4 Nanotherapy Drugs. Mater. 2021;14(8):1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14081824.
Kerroum MA, Essyed A, Iacovita C, et al. The effect of basic pH on the elaboration of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation method: Structural, magnetic and hyperthermia characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019;478:239-246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.01.081.
Dabbagh A, Hedayatnasab Z, Karimian H, et al. Polyethylene glycol-coated porous magnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics under magnetic hyperthermia condition. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):104-114. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2018.1536809.
Oltolina F, Peigneux A, Colangelo D, et al. Biomimetic Magnetite Nanoparticles as Targeted Drug Nanocarriers and Mediators of Hyperthermia in an Experimental Cancer Model. Cancers. 2020;12(9):2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092564.