Preparation and Application of Cross-linked Alginate Nanoparticles as Drug Carrier: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.5.1.111Keywords:
Alginate nanoparticle, Gelation technique, Emulsification technique, Drug carrier, Cross-linked biopolymerAbstract
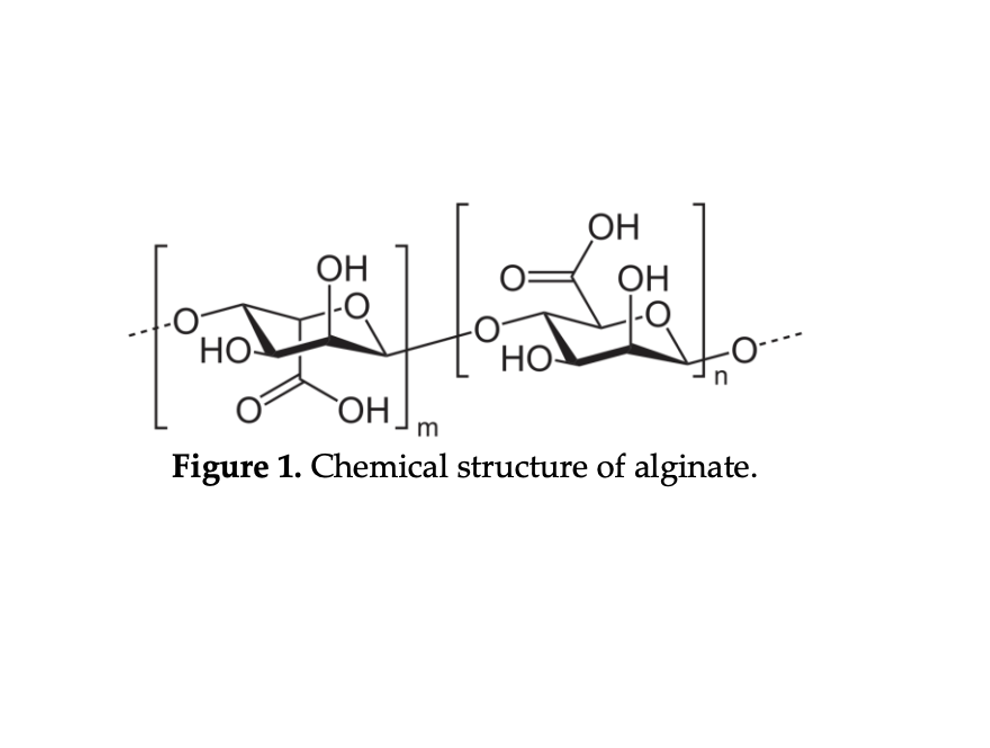
Nanotechnology also called as nanotech is referring to the science, technology and engineering to synthesis, manipulation and investigation of materials and devices at nanoscales. Nanoparticles (NPs) owns a special place in nanotechnology due to their extreme-small size, multifunctionality, and modifiable surface for wide range of applications especially in new drug delivery application as the stability, solubility, biocompatibility and drugs releasing of NPs are highly controllable. The variation of nanomaterials with different physiochemical and morphological properties will affect the materials-living cells interaction and determination of the route of clearance and potential toxic effects. Thus, it requires more cross-disciplinary research on the designing and developing of drugs delivery NPs based on the diagnosis and treatment of devastating diseases. Biopolymers-based NPs have gained great attention for drug delivery system over the past few decades compared to other materials-based NPs such as liposomes, ceramics and lipids as well as magnetic NPs. There are extensive studies and developments of biopolymers-based NPs for drug delivery and tissue engineering as it capable of controlling the release of drugs, stabilizing labile molecules from degradation, and site-specific drug targeting. Alginate is an anionic copolymer that extracted from algae. The NPs composed alginate have become one of the most extensively researched materials for biomedical applications such as tissue engineering, wound dressing, protein/enzyme carrier and drug delivery due to its biodegradability, biocompatibility, non-toxicity and mucoadhesive properties. Furthermore, by physiochemical crosslinking and cooperating with other polymers, the mechanical strength, cell affinity and drug release profile can be modified and improved. In this brief review paper, several aspects about using alginate or crosslinked alginate for drug delivery application will be discussed, mainly focus on the structure and properties of alginate such as biocompatibility, immunogenicity and biodegradability, as well as the effect of mucoadhesion and pH sensitivity of using alginate in drug delivery nanoparticles developments.
Downloads